PLEASE NOTE: The information in this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider if you’re seeking medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Despite being part of the human diet for millions of years, eggs are one of the most debated foods in modern history. They have been the subject of a decades-long campaign by food critics, health organizations, and even governments.
How could this be? Let’s find out.

In this article, we’ll look at:
- Why eggs have been criticized
- 10 health benefits of eggs
- The best ways to incorporate eggs into your diet
- How to shop for high-quality eggs
Off we go!
Egg Nutrition Facts: Are Eggs A Good Source of Protein?
Despite their small size, eggs pack a punch nutritionally. One large egg contains approximately …
- 6g of protein
- 5g of fat
- 0.5g of carbs
- 70 calories
Eggs are also a source of high-quality protein, antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids (1). These nutrients can be valuable for pregnant women, children, the elderly, and for athletes (2).
Both the egg yolk and white offer important benefits. Egg yolks have about 40% of the protein and provide more protein, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, and selenium (3, 4). Meanwhile, egg white offers more magnesium, potassium, and sodium.
Despite this, the potential health benefits of eggs are often overlooked.
10 Health Benefits of Eggs
Given their low cost and impressive nutrition facts, eggs are consumed globally. Here are 10 potential health benefits of eggs:
1. Nutrient Density
A critical health benefit of eggs is their nutrient density.
Just 2 eggs per day can satisfy 10-30% of human vitamin requirements (5). Eggs even contain all vitamins (except for vitamin C). Eggs are also one of the few natural food sources of vitamin D (6).
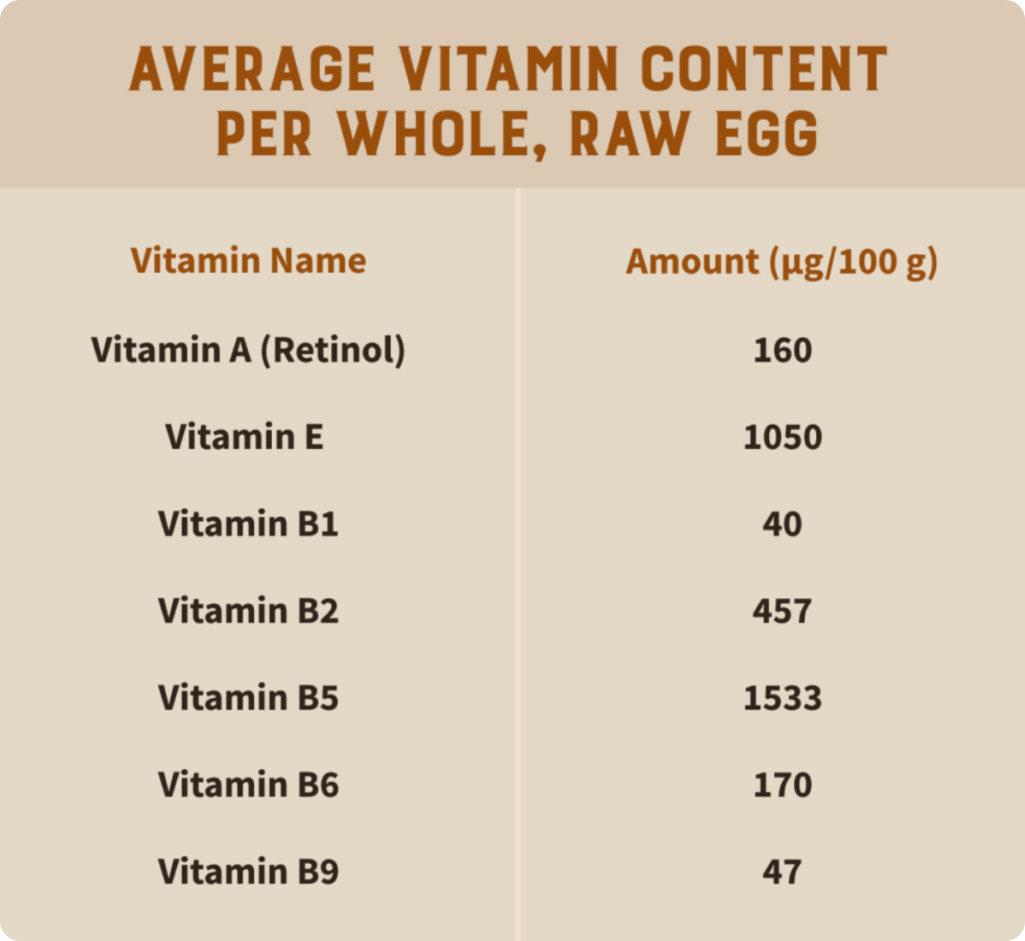
In addition to vitamins, eggs offer a host of valuable minerals such as magnesium, iron, calcium, sodium, zinc, potassium, and phosphorus (7). But it doesn’t stop there. Eggs also contain all 9 essential amino acids and omega 3 fatty acids (8, 9).
Many of these components are thought to protect against chronic disease and may provide antimicrobial and anticancer effects (10, 11).
2. Weight Loss
Obesity is a global health issue that is connected to type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease (12).
Compared to other protein sources, eggs can be incredibly filling (13). This is one reason why eggs may be helpful for weight loss, appetite control, and weight management (14, 15). Eggs have also been shown to be helpful for the body mass index (BMI) of healthy people (16).
3. Eye Health
DHA and carotenoids are both naturally present in eggs and are crucial for eye health (17). Two carotenoids in eggs, zeaxanthin and lutein, are thought to help reduce cataract formation and macular degeneration (18, 19, 20).

4. Bone Health
Regular consumption of eggs is being explored as a strategy to promote bone health (21). Eggs contain compounds that may positively influence bone mineral density (22).
Vitamin D (found in egg yolks) is known to assist the promotion of bone health (23, 24). Another mineral found in eggs, zinc, supports bone repair and formation along with the creation of collagen.
5. Brain Function
Nutrients found in eggs can also benefit the brain, memory function, and cognition (25). Some of these nutrients include:
- Choline, a neurotransmitter that’s involved in cognitive function and memory (26, 27).
- Protein, amino acids, and carotenoids may protect against cognitive decline (28).
- B vitamins can assist brain development (29).
Eggs (along with beef liver and kidney) offer one of the richest sources of choline (30). Despite its importance, up to 90% of adults may not be getting enough of this essential nutrient (31).
6. Gut Health
Due to the presence of butyrate and propionic acid, consuming eggs may promote and maintain a healthy gut lining (32).
7. Immune Function
Nutrients in eggs, such as vitamin B12, vitamin D, selenium, and choline, also influence immune function (33, 34, 35).
8. Muscle Building
Along with a healthy diet and exercise, eating eggs can be a helpful tool to improve your body composition.
Protein provides nitrogen and amino acids that are required for energy and tissue growth (36). As a nutrient dense source of protein, eggs can help support and increase muscle mass (37, 38, 39).

A randomized control trial from 2021 found that compared to young males just eating the egg whites, whole egg consumption can improve muscular strength, testosterone levels, and body fat percentage (40).
9. Cardiovascular Health
As you’ll learn below, eggs have been viewed for decades as a potential contributor to cardiovascular disease due to their cholesterol content. However, dietary guidelines have been revised, and this view has been changing (more on this later) (41).
In fact, the B vitamins, essential amino acids, and other nutrients in eggs may offer protection against CVD (42). Studies have even shown that regular egg consumption can be beneficial for blood pressure (43).
A study on over 500,000 Chinese adults noted that compared to those who rarely ate eggs, daily egg consumption was associated with a decreased risk of CVD (44). Another large meta-analysis of almost 2 million people found no association between CVD mortality and high intake of eggs (45).
10. Digestibility
Along with dairy and meat, eggs are a highly digestible protein source (46). As an added bonus, almost all of the nutrients in a chicken egg are put to use by the body, given their bioavailability (47).
What About Cholesterol?
A lingering concern about eggs is their high cholesterol content and the potential consequences on heart health.
In 1968, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommended that people consume no more than 3 eggs per week and less than 300mg of dietary cholesterol daily (48). Since then, the idea that dietary cholesterol increases blood cholesterol levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease has stuck around.
But is this actually true?
In 2015, the USDA revoked its restriction on egg intake and on the upper limit for dietary cholesterol intake (49). Recent evidence has also shown that eggs don’t appear to be risky when consumed in a healthy diet (50, 51).
Here are some key findings:
- A long-term population study on over 117,000 people found no difference in cardiovascular disease risk for those eating 1 egg per day compared to 1 egg per week (52, 53)
- “We failed to find any significant association between egg consumption and risk of CVD mortality.” (54)
- “The results from our cohort study and updated meta-analysis show that moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) is not associated with cardiovascular disease risk overall.” (55)
- “Results from the Framingham Study showed no significant association between the number of eggs consumed with all-cause mortality, total coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, or angina pectoris.” (56)
While eggs are a major source of cholesterol (about 200 mg per egg), cholesterol from the diet can have little to no impact on cholesterol levels (57, 58). About 75% of cholesterol is made within your body, and around 25% comes from the diet (59, 60).
Eggs have been singled out for decades as a culprit for cardiovascular disease, but this idea is seriously in question (61).
How to Incorporate Eggs Into Your Diet
Not only are eggs a valuable source of vitamins and minerals, but they’re also cost-effective and can be consumed in dozens of different ways. Aside from the classic options like hard-boiled or scrambled eggs, you can also try:
- Quiche
- Breakfast casserole
- Frittata
- Deviled eggs
- Omelets

If you’re on an animal-based diet, these can be an exciting way to spice up your breakfast options. Eggs are also helpful for baked goods and even for recipes like fried rice.
Due to so many options on the shelf, shopping for eggs can seem daunting. It may not be as simple as just reaching for a carton of organic eggs. But you can find high-quality eggs at just about any grocery store, as well as local farmers’ markets.
Here’s a quick guide that breaks down common phrases you’ll find when buying eggs:
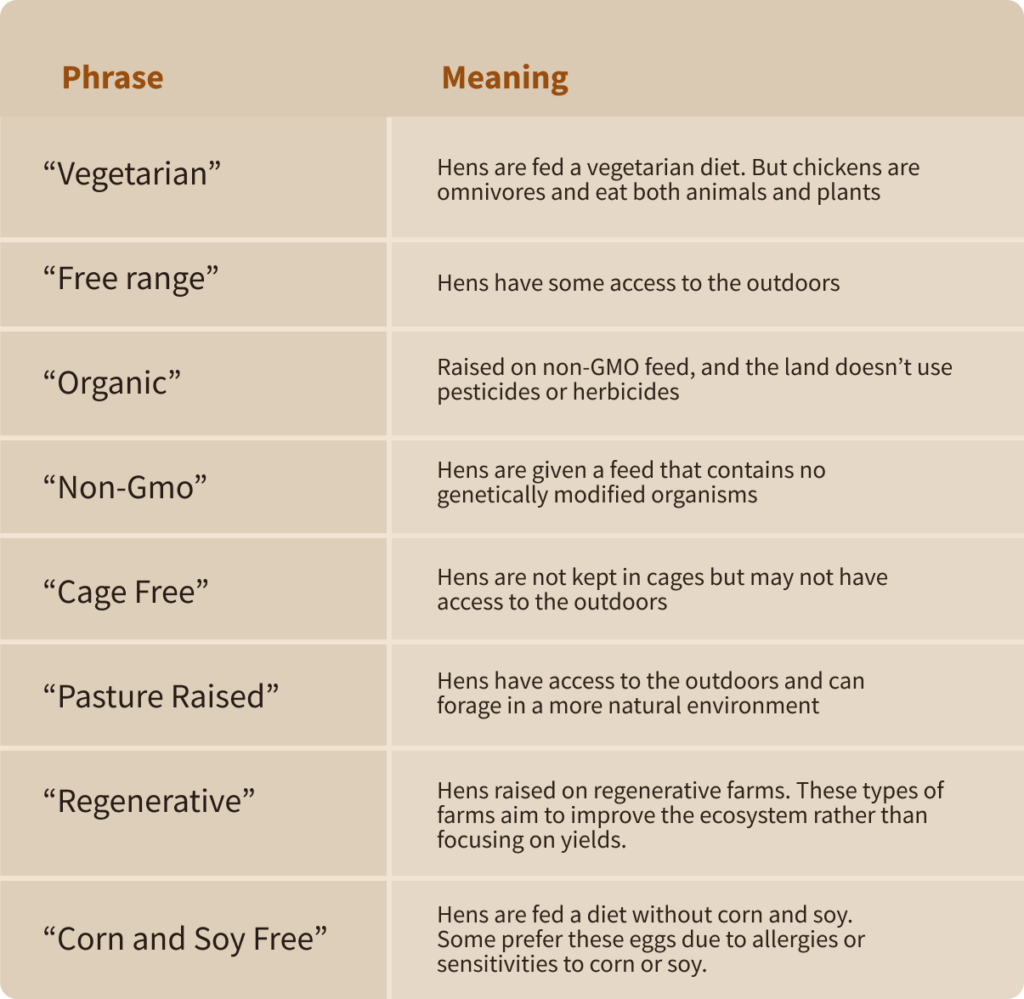
Many of these terms are vague and intentionally misleading, making it difficult to find the highest-quality eggs. One of the best ways to understand the animal’s diet, living conditions, health, and other important information is to discuss it with a local farmer.
The Bottom Line: Eggs Are Nutritious, Flexible, and Cost-Effective
Like so many other animal foods, eggs have been ridiculed for decades, yet the tide is turning, and their true value is being recognized once again.
Although their reputation is still recovering from the hysteria of the 1960s, eggs are highly nutritious. As a helpful source of protein, vitamins, and minerals, eggs can positively impact numerous aspects of your health.
Fat Loss Stack
Grass-Fed Organs for Metabolic Health
Subscribe to future articles like this:
