Chances are you or someone you love has been impacted by an autoimmune disease, given they occur in an estimated 3-5% of the population (1). Autoimmune challenges can be incredibly taxing on both mental and physical health. But your quality of life doesn’t have to suffer when living with one of these challenges.
While medications and other medical practices can be helpful, many people are left to believe that these are the only options. This is not the case.
We frequently work with people who see dramatic improvements in their autoimmune symptoms through diet and lifestyle choices. Paul Saladino, MD, even got rid of his eczema following many of the suggestions below!
In this article, we’ll discuss:
- Contributing factors to autoimmune disease development
- Nutrients and foods to prioritize when managing an autoimmune disease
- The importance of removing processed foods, plant-defense chemicals, and toxins
- Lifestyle practices to support your immune system
Off we go!
What is an Autoimmune Disease?
When functioning optimally, the immune system defends against infection or disease. With autoimmune diseases, immune function is compromised, and your cells, tissues, and organs are attacked.
Over 100 autoimmune diseases can impact different organs or tissue types, such as the skin, the thyroid, or the gut.
Here are some common autoimmune conditions:
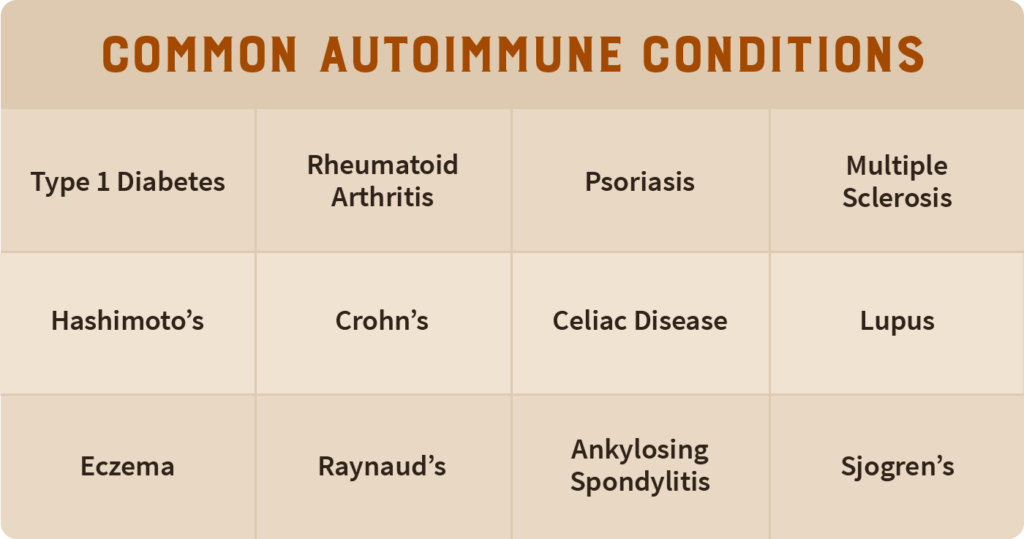
A lot of these overlap, and many people have multiple autoimmune disorders at once. They also primarily impact women (2). We are even beginning to see people with autoimmune syndromes that do not have specific definitions in Western medicine, regardless of the same process is going on underneath the surface.
It’s usually our body’s immune system attacking our cells (friendly cells) incorrectly, so we have to ask: Why has the immune system started attacking our friendly cells?
Where Do Autoimmune Diseases Come From?
The exact cause(s) of autoimmune diseases is unknown. Still, a variety of factors can contribute to their development, such as:
- Genetics (3)
- Gut Dysbiosis (4)
- Pathogens (viruses, yeast, bacteria) (5)
- Exposure to heavy metals, chemicals, and pesticides (6)
- Stress (7)
- Organic Solvents (paint thinner, nail polish, detergents, etc.)(8)
Based on these triggers, it should be clear that diet and lifestyle choices are paramount when looking to improve an autoimmune disorder.
First, let’s take a look at important dietary considerations!
The Importance of Meat and Organs
We suggest making well-raised meat and organs the centerpiece of your diet, as the average American consumes inadequate amounts of key nutrients (most of which are plentiful in animal foods)(9,10).
These inadequacies can impair immune function and contribute to many chronic diseases that we see today, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and more (11, 12).
Many nutrients in organs aren’t found in significant amounts in muscle meat or plant foods, so bringing organs into the mix provides essential nutrients for optimal health.
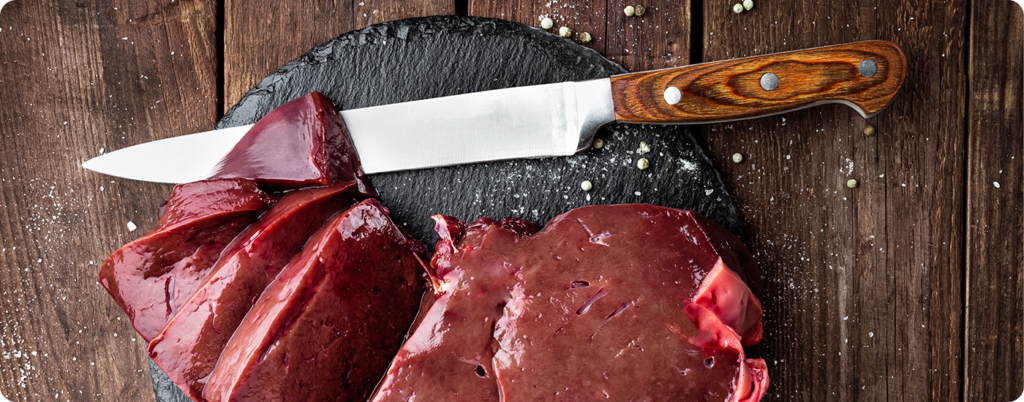

Red meat and organs (like liver, heart, kidney, and the thymus in particular) contain robust amounts of vitamins, like A, D, E, B6, B12, and folate, and minerals, like zinc, iron, copper, selenium, and magnesium, in their exact forms they exist inside our bodies.
We focus mainly on grass-fed and grass-finished ruminant animals (cattle, buffalo, goat, lamb, deer). Our concerns with grain-finished meat come down to the feed quality these animals consume. The grains which make up cattle feed are often sprayed with pesticides like glyphosate and atrazine. Feel free to check out this article for additional details on constructing an animal-based diet.
Critical Nutrients for the Immune System
Vitamins A and D can be particularly important for autoimmune diseases (and general well-being).
Vitamin D is a natural immune modulator, and reduced levels have been implicated in autoimmune diseases (13).
We prefer sun exposure and whole food sources instead of vitamin D supplementation when possible. Exposure to direct sunlight and UV promotes Vitamin D and nitric oxide synthesis in the skin, which helps regulate hormones, decrease blood pressure, and increase blood flow throughout the body.
Food such as liver, eggs, and wild-caught fish can also contribute small amounts.
Vitamin A impacts many areas, such as the skin, gut, and eyes. It also plays a role in proper immune function and defense against infectious diseases (14). As noted above, many individuals don’t meet dietary requirements for this crucial vitamin.
The good news is that a small amount of liver can help close this gap, as one ounce contains about 150% of the RDA for vitamin A (15).
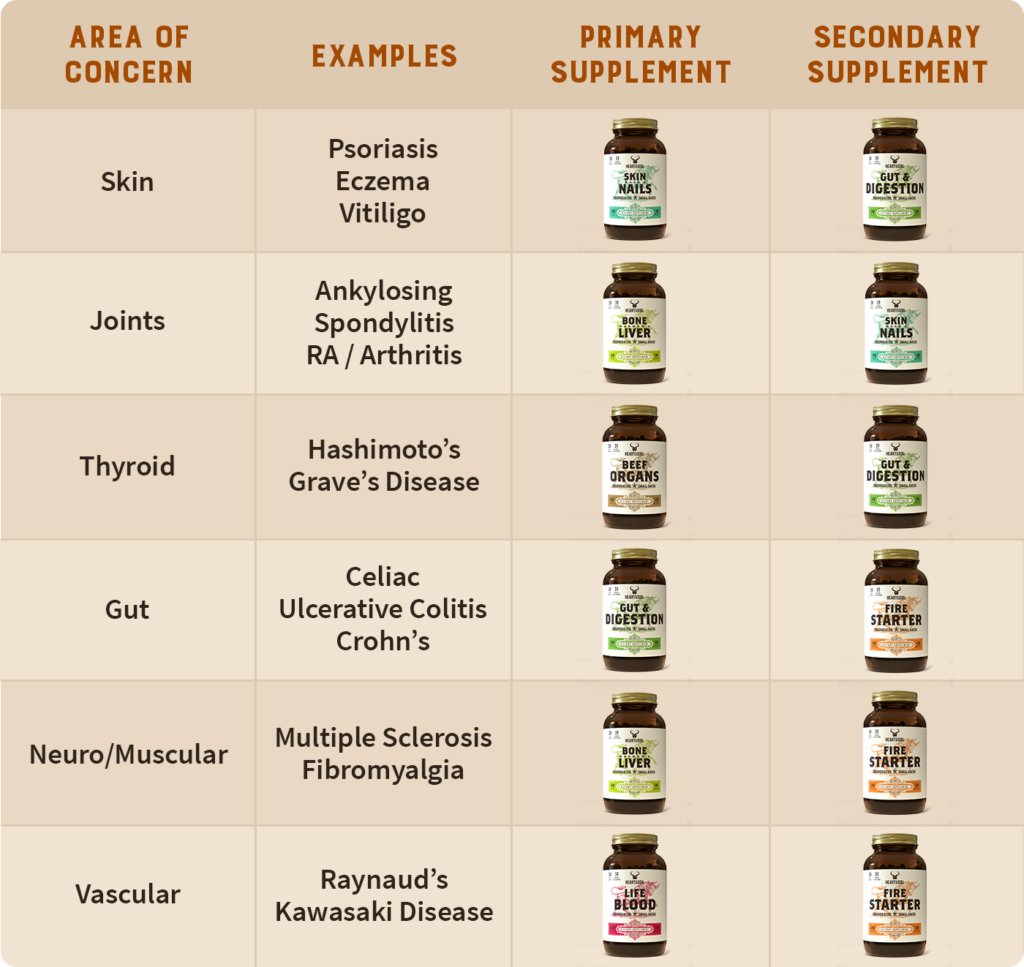
Our supplements are a great alternative if you don’t have access to fresh liver. Here’s a quick guide that shows the most popular Heart & Soil supplement selections for different areas affected by autoimmune disease:
It’s essential also to avoid certain foods and environmental exposures!
4 Things to Avoid When Fighting Autoimmune Disease
We have seen many clients improve their autoimmune symptoms by including nutrient-rich animal foods and eliminating seed oils and the most offensive plant foods (leaves, stems, seeds, nuts, grains, nightshades, and legumes).
It can also be helpful to cut out processed foods such as vegetable oils and reduce your exposure to toxins.
1. Processed Foods

One of the key principles of the animal-based diet is the removal of highly-processed foods. While they may taste great, many processed foods are devoid of nutrients. They’re also likely to include seed oils, artificial sweeteners, or other potentially troublesome ingredients.
2. Seed Oils
As mentioned earlier, avoiding vegetable oils (corn, safflower, sunflower, soybean, cottonseed, canola, peanut, etc.) that contain unnatural amounts of linoleic acid is especially important. This level of linoleic acid intake can promote autoimmune disease and other health issues (16, 17).
It can also be helpful to cut out meat from animals primarily fed corn or soy, such as conventionally raised beef, chickens, pigs, turkey, and ducks.
Unlike ruminant animals, monogastric animals (chickens, pigs, turkeys, ducks, and humans!) can’t get rid of excess amounts of linoleic acid (polyunsaturated fatty acid, also found in vegetable oils) from their diets, and it accumulates in their fat over time.
When consumed in excess, this molecule can be highly damaging to our mitochondria leading to inflammation and chronic disease if not appropriately addressed. So, we suggest cutting these out or finding corn-and-soy-free alternatives, such as those from White Oak Pastures or Nose To Tail.
3. Plant Defense Chemicals
We believe that the elimination (or reduction) of plant toxins can be extremely beneficial for those with autoimmune diseases.
Many plant foods don’t want to be eaten, and to protect themselves; they produce defense chemicals that can harm our health, especially if consumed in excess.
Things like lectins, oxalates, and other plant defense chemicals can irritate the gut. So, removing (or limiting) these from the diet can also benefit the immune system.
Lectins are a type of protein that can interfere with cellular communication and can lead to GI upset, weight gain, fatigue, and other challenges (18). Large amounts of lectins can be found in nuts, seeds, grains, legumes, and nightshades.

Oxalates are another defense chemical commonly found in potatoes, leafy greens, chocolate, almonds, and turmeric. If consumed in excess, it may cause various symptoms, including kidney stones, chronic fatigue, arrhythmias, insomnia, joint pain, digestive issues, and much more (19, 20, 21, 22, 23).
Feel free to check out our animal-based infographic and a couple of podcasts to add further clarity on this topic. The first explores the various toxins found in plants in granular detail, and the second gives a general overview of the toxicity spectrum.
4. Toxins

Another key focus should be toxin reduction, as autoimmune disease appears to be heavily influenced by your environment. We’re constantly exposed to toxins through plastics, drinking water, food, the air, and household products (24).
Thankfully, lifestyle changes can drastically reduce your exposure. Some simple tips include:
- Water filtration
- Choosing cleaner personal care products
- Choosing organic foods
- Cutting out alcohol and cigarettes (25)
- Eliminating as many plastic products as possible (water bottles, pans, utensils, etc.)
Additionally, it can be helpful to work with a functional medicine practitioner or other medical professionals when addressing these toxins (or autoimmune diseases in general). Many will develop personalized protocols for removing heavy metals, mold, or other environmental toxins.
Let’s now look at lifestyle practices to support your immune system!
Lifestyle Habits to Improve Your Autoimmune Disease
Each suggestion aims to minimize stress and boost the immune system.
Prioritize Sleep
Sleep optimization is crucial for the immune system (26, 27). Our main suggestion is to include bone broth and connective tissue in the diet. These foods contain an amino acid called glycine which plays several roles in our physiology (28). Glycine serves as a neurotransmitter in the brain and lends itself to proper relaxation and achieving deep sleep (29).
Exercise
It is essential to complete some level of physical activity daily. The minimum suggestion we give is two or three 10-minute walks pre/post-meals. Bonus points for adding in some weights for strength training!
Manage Stress
We challenge everyone to engage in some stress management activity. Meditation, prayer, sitting outside and connecting with nature, gardening, or even learning a new skill can all be enjoyable ways to reduce stress (30, 31, 32).
Exposure to Sunlight
Remember to get outside, play in the sun, and reconnect with nature.
Daily sun exposure can help the body enter its natural circadian rhythm cycle, which promotes sleep (33) and recovery. Sun exposure has also been shown to improve alpha diversity of the gut (34).
Sauna and Cold Exposure
Heat exposure enhances several of our bodies’ detoxification pathways, up-regulates glutathione production, and enhances mitochondrial adaptation.
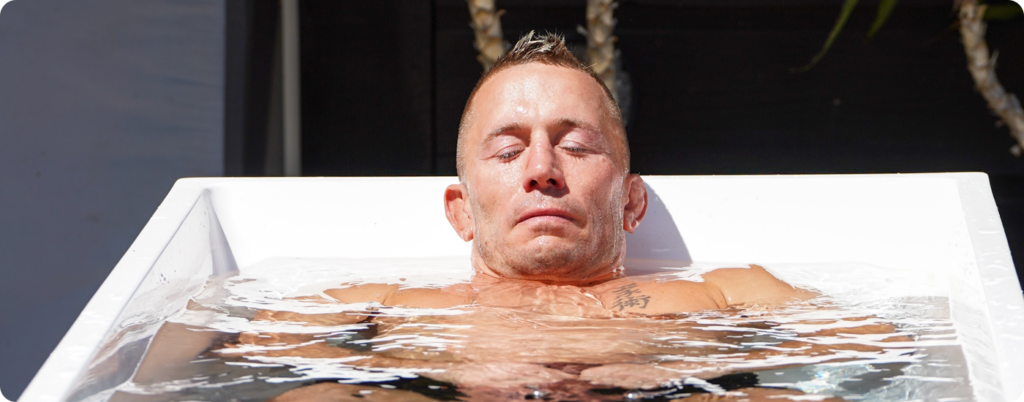

Cold exposure (cold showers or plunges) can also dramatically improve the immune system and vascular health (35, 36, 37, 38).
Autoimmune Disease: The Good News
Autoimmune diseases have become incredibly common. They can affect various areas such as the skin, gut, thyroid, or a combination of multiple.
While the exact cause(s) of autoimmune disease is unknown, the good news is that your diet and lifestyle choices can positively impact your condition.
Many people have improved their conditions by removing processed foods and prioritizing high-quality meat and organs. These people also benefited from reducing toxins, managing stress, prioritizing sleep, and improving other lifestyle habits.
Your quality of life doesn’t have to suffer when managing an autoimmune disease! The body is capable of incredible healing with consistency, time, and simple changes.
Autoimmune Issues Stack
Restore Balance To Your Immune System
Subscribe to future articles like this:
