PLEASE NOTE: The information in this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider if you’re seeking medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
As interest in elimination diets and ancestral eating patterns continues to grow, another popular diet has entered the ring: the meat and fruit diet. Just like the ketogenic diet, carnivore, and paleo, this way of eating was popularized by big names such as Joe Rogan and Paul Saladino, MD.

This simple yet controversial diet eliminates most plant foods while maintaining access to nature’s candy—fruit—alongside nutritious animal proteins. Even with the addition of fruit, the question remains: Is it actually better than the typical low-carb diet? Let’s find out.
In this article, we’ll explore what to eat and avoid on the meat and fruit diet, examine its potential health benefits and risks, and compare it to other popular dietary strategies to help you make informed decisions about your nutritional journey.
What is The Meat and Fruit Diet?
The meat and fruit diet limits food choices to animal protein and fresh fruit, with an emphasis on meat from ruminant animals like beef, bison, or lamb.
Although it’s recently been popularized by people like Joe Rogan and Paul Saladino, MD, the meat and fruit diet draws inspiration from evolutionary dietary patterns, recognizing that meat consumption has been a cornerstone of human nutrition and evolution for millions of years (1).

Meat has been cherished by human communities as a nutritious and highly symbolic food throughout our evolutionary history. The addition of seasonal fruits to this foundation reflects how our ancestors would have supplemented their animal-based nutrition with fresh fruit.
Compared to a ketogenic, carnivore, or paleo diet, the meat and fruit diet can be more approachable thanks to its increased flexibility. This makes it more appealing to athletes and those looking to avoid the pitfalls of low-carb diets (more on this below).
What to Eat & Avoid on the Meat and Fruit Diet
Unlike the keto diet, which has dozens of restrictions, the meat and fruit diet is very simple to follow. Here’s what you can eat and what is generally avoided:
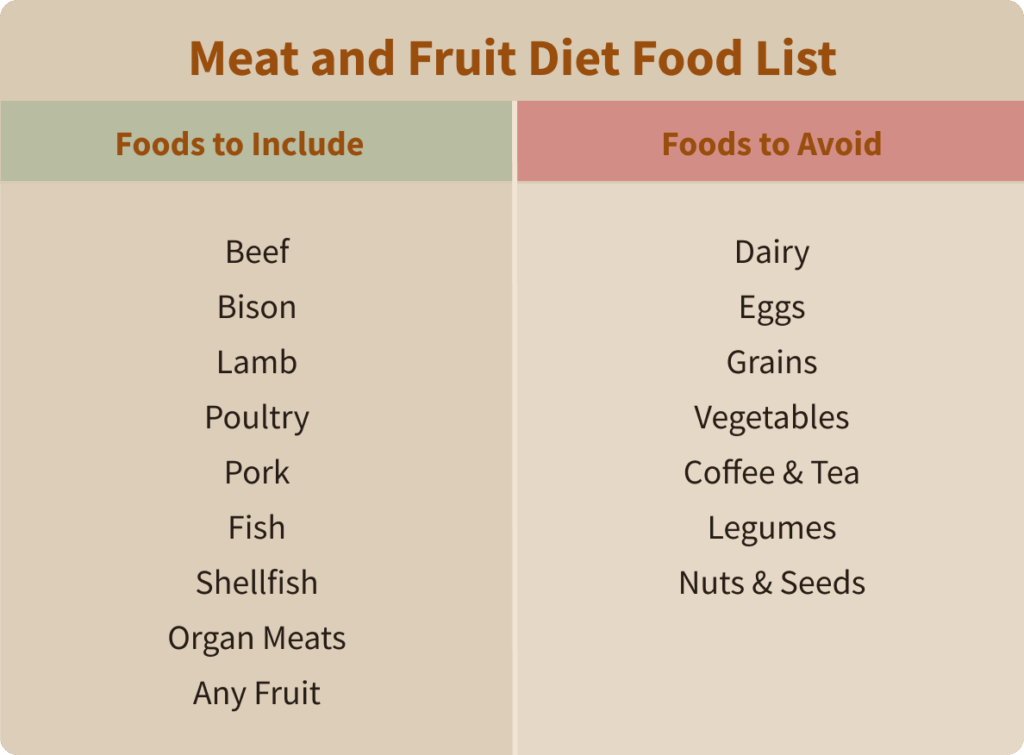
Foods to Include
All forms of meat are typically permitted, including beef, pork, lamb, poultry, fish, and shellfish. In particular, many followers of this diet choose to prioritize red meat (beef, bison, lamb, etc.) as they can be especially nutritious, offering high-quality protein, B vitamins, and trace minerals (2, 3).
Beef Organs
Nature's Ultimate Multivitamin
Although they’re often overlooked, organ meat such as beef liver can be a vital addition to the meat and fruit diet. Organs are particularly reliable sources of vitamin A, iron, zinc, folate, selenium, choline, and other valuable nutrients (4, 5).
Organ meats are readily available at local farmers’ markets and grocery stores like Sprouts or Whole Foods. If you don’t have access to fresh organs or don’t enjoy the taste, supplements from Heart & Soil are a simple alternative.
Our organ supplements are 100% sourced from regeneratively raised, grass-fed & finished cattle, and free from hormones, pesticides, and artificial ingredients.
Fresh, frozen, or freeze-dried fruit is another staple of the meat and fruit diet. Fruits are an important source of carbohydrates, polyphenols, antioxidants, and other nutrients (6, 7).
Red fruits are especially beneficial, as they are recognized as good sources of many bioactive ingredients and nutrients, including vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin E, minerals such as phosphorus, iron, magnesium, potassium, sodium, manganese, and copper, plus dietary fiber and antioxidants (8).

Foods to Avoid
The meat and fruit diet eliminates all vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and ultra-processed food. This means avoiding leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, root vegetables, and all forms of cereals and grain-based products.
Even dairy products, eggs, certain oils, and condiments are also typically restricted, though some variations of the diet may allow certain animal-derived fats.
The Hidden Dangers of Low-Carb Diets
While the meat and fruit diet can provide many essential nutrients, careful attention must be paid to potential nutritional gaps left from the absence of dairy, eggs, and certain vegetables. Although this way of eating isn’t always as low in carbohydrates as a keto, paleo, or carnivore diet, it may have similar dangers, such as:
- Adaptation Challenges: During the initial adaptation period, many people experience symptoms including fatigue, headaches, nausea, dizziness, constipation, and reduced exercise tolerance (9).
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Low-carbohydrate diets are often low in fiber, thiamine, folate, vitamins A, E, and B6, calcium, magnesium, iron, and potassium (10).
- Long Term Challenges: potential risks including kidney stone formation, altered liver biochemistry, changes in thyroid function, and increased risk of bone loss and fractures (11, 12, 13, 14).
- Sustainability: restrictive diets can be difficult to follow during certain relationships, social settings, or during travel (15).
For these reasons, the meat and fruit diet may only be a stepping stone for most people as they seek fewer restrictions and more sustainability.
The Animal-Based Diet: The #1 Alternative to The Meat and Fruit Diet?
Thanks to a variety of short and long-term challenges, many low-carb dieters end up moving to a way of eating known as the animal-based diet. Even Paul Saladino eats this way full-time, and Joe Rogan has experimented with it as well.
This way of eating consists of high-quality animal foods such as meat, organs, eggs, raw dairy, fruit, honey, and other low-toxicity plant foods.

Although it’s similar to the meat and fruit diet, the animal-based diet offers greater flexibility as it allows for more animal-based foods such as dairy, eggs, honey, and even certain grains and vegetables. The main foods that the animal-based diet eliminates are ultra-processed junk food, seed oils, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
The nutrient density and added flexibility of the animal-based diet make it extremely versatile for athletes and have even helped with health goals such as improved gut health, weight loss, and increased energy levels.
Download the full animal based diet food list PDF for a printable animal-based grocery list and other resources to help you get started.
The Bottom Line: The Meat & Fruit Diet is Trendy, But Not Ideal
The meat and fruit diet is a trendy strategy often used by those looking to improve food sensitivities, autoimmune conditions, and other tricky health challenges. This diet combines the exceptional nutrient density of animal proteins with the natural sugars and micronutrients found in fruits.
While this dietary pattern may offer benefits over extremely restrictive approaches like strict carnivore diets, the meat and fruit diet may still present challenges in terms of nutritional completeness and sustainability.
Instead, the animal-based approach can offer many of the same benefits with added flexibility and potentially better long-term outcomes.
Subscribe to future articles like this:

