PLEASE NOTE: The information in this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider if you’re seeking medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
If you found this article, it’s likely that your health isn’t where you want it to be. Maybe you’re looking to lose weight, kick food sensitivities, or be able to make it through the day without needing a nap.
When looking to improve health struggles with better food choices, the keto vs carnivore diet debate is sure to make an appearance. This article walks you through the ins and outs of each diet, alternatives, and tips for success if you decide to try a keto or carnivore diet.
Off we go!
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
Initially used as a method to treat epilepsy, the ketogenic diet is now promoted as a solution for weight loss, migraines, brain enhancement, type 2 diabetes, and other challenges (1, 2).
Considered one of the most popular low-carb diets, the ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low carb diet with around 20-50 grams of carbs per day (3).
The ketogenic diet limits or removes ultra-processed foods and other high-carb food sources, such as rice, pasta, bread, starchy vegetables, and fruits high in sugar. These are some of the most commonly consumed foods on a ketogenic diet:
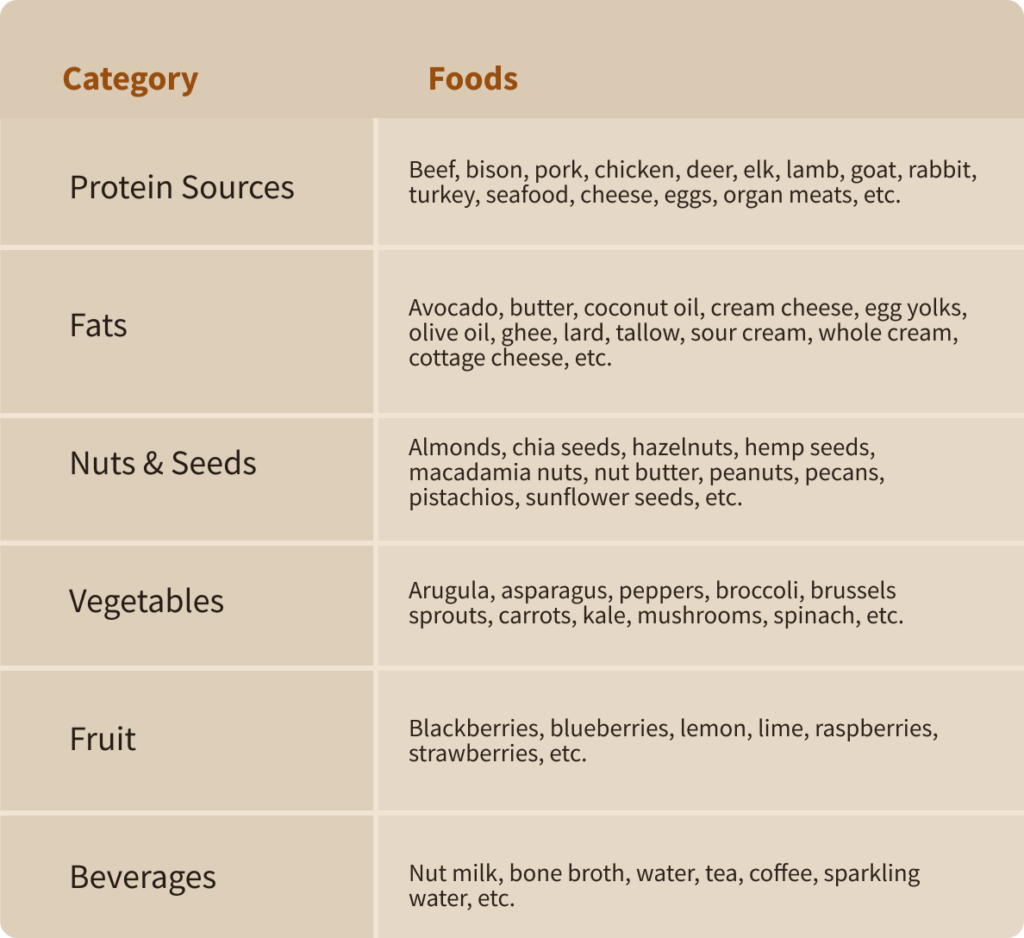
Carbohydrate restriction as part of a ketogenic diet can cause your body to enter ketosis and create ketone bodies (4, 5). While your body usually utilizes carbohydrates and glucose, these ketones are then used by the brain and other parts of the body as their main source of energy (6, 7).
What is the Carnivore Diet?
Widely popular, yet equally controversial, the carnivore diet focuses solely on animal foods like meat, seafood, organs, eggs, and dairy. The carnivore diet excludes fruit, vegetables, grains, nuts and seeds, alcohol, soda, and other high carb food sources.
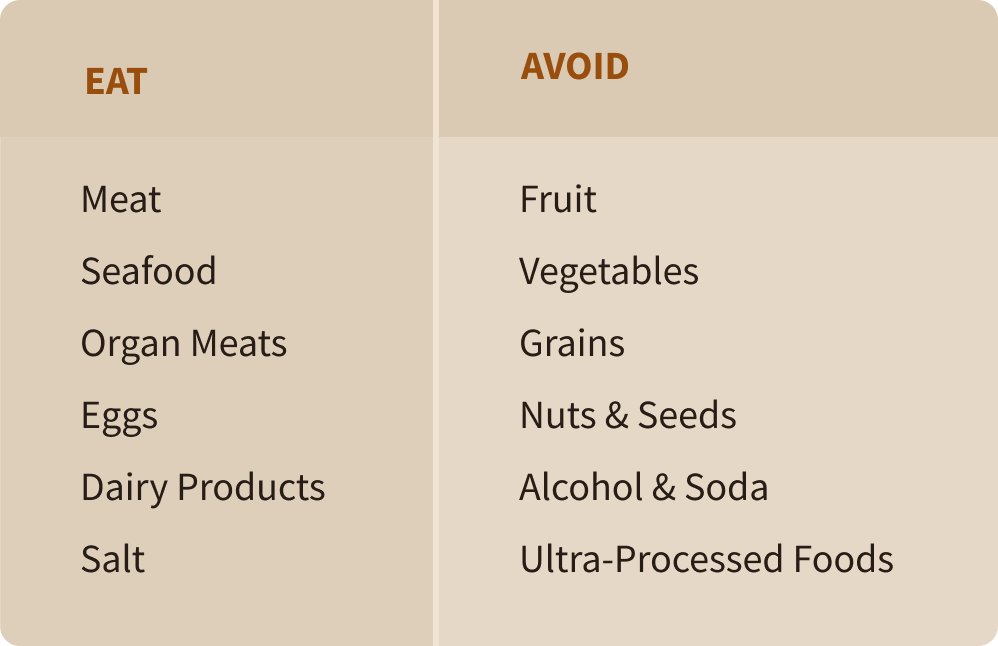
Although it seems extreme, the carnivore diet is a popular short-term elimination diet aimed at improving gut health, autoimmune conditions, weight loss, and various other health challenges (8). Both the carnivore and keto diet are being explored as potential treatment options for inflammatory bowel disease (9).
If you’d like further guidance, download the printable carnivore diet food list and 5-day meal plan.
Keto vs Carnivore: Which Should You Choose?
Carnivore and ketogenic diets have key similarities.
- They limit carbohydrate intake
- They prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods
- Consumption of ultra-processed food is discouraged
- Animal products are prioritized
At the same time, these two diets can result in a dramatically different experience. Here are the major differences between a ketogenic and a carnivore diet.
Flexibility & Food Selection
Given that the ketogenic diet includes more than just animal based foods, it offers more flexibility with a variety of protein, fat, fruit, and vegetable options to choose from. The keto diet is also known for having thousands of products for snacking ranging from protein bars, desserts, drinks, crackers, and more.

One key difference between the ketogenic and carnivore diets is the role of plant based foods. Since the carnivore diet removes all plant foods, this also leads to a dramatic reduction in antinutrient intake.
Known as antinutrients, plants contain synthetic compounds that can hinder nutrient absorption and offer protection from the surrounding environment (10, 11). When consumed in excess, antinutrients found in plants may cause harm. The avoidance of antinutrients such as oxalates, lectins, and phytates is one popular reason for choosing the carnivore diet instead of the ketogenic diet.
Cost
Although the carnivore diet only includes animal foods, it can actually be cheaper than a ketogenic diet.
Animal foods are not exactly the cheapest foods at the grocery store, but the carnivore diet essentially eliminates money spent on snacks like protein bars or expensive meals at restaurants. Animal foods are also extremely filling, meaning many carnivore dieters consume less food overall.
The carnivore diet also has the added benefit that foods like ground beef or eggs can be bought in bulk or at a discounted price from local ranchers.
Risks
The risks associated with following a carnivore or ketogenic diet are similar. The main concerns are nutrient deficiencies, electrolyte imbalances, reduced exercise performance, and difficulties while transitioning.

The long-term impact of ketosis and a low carbo is not clear yet. But serious challenges such as kidney damage, osteoporosis, and heart arrhythmias have been reported (12).
Even though animal foods are a valuable source of nutrients, some carnivores or keto dieters may not be getting enough vitamin C, vitamin E, magnesium, potassium, calcium, iodine, and other crucial nutrients (13).
Scientific Understanding
Unlike the ketogenic diet, which has been studied for decades given its utility against epilepsy, the carnivore diet is recently garnering traction in scientific literature. Much of the data around the carnivore diet is anecdotal, although it has shown promise for mood, energy levels, digestive issues, and mental clarity (14).
The ketogenic diet has shown benefits for weight loss, improved glucose control, and may reduce the risk of heart disease (15, 16).
5 Tips for Transitioning to a Low-Carb Diet
Diets like carnivore or keto can lead to numerous benefits, but transitioning to them can be an unpleasant experience for some. Low-carb dieters can experience a host of short or long-term challenges, such as:
- The “keto flu” includes symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, dehydration, headache, nausea, and other flu-like symptoms (17, 18).
- Nutrient deficiencies (19, 20).
- Reduced exercise performance (21, 22).
- The benefits of low-carb diets may diminish after about 6 months to 2 years (23, 24).
- Traveling, relationships, and social events can make it challenging to remain committed to a low-carb diet.
Here are 5 tips to help this transition go more smoothly.
1. Transition Slowly
Rather than jumping straight into a strict carnivore diet overnight, it can be helpful to slowly remove foods. This enables your body to adapt to the changes, and you may even discover that you don’t need to follow a highly restrictive diet to feel your best.
2. Work With A Medical Professional
Given the risks of nutrient deficiencies and other challenges, working with a medical professional can increase your chances of success.
It may be useful to conduct regular testing to identify any existing deficiencies or underlying health conditions that may be present. They can also help you with strategic supplementation.

3. Focus on Variety
Part of the appeal of a carnivore or ketogenic diet is its simplicity. But this simplicity may lead to a lack of variety and essential nutrients. For both of these diets, it can be useful to include a wide range of protein options from different meats, seafood, eggs, and even wild game.
Dairy and organ meats can also offer additional nutritional value.
If a low-carb diet doesn’t include dairy or organ meats, you may not be getting enough calcium, vitamin A, vitamin C, or vitamin E (25, 26). The carnivore diet may not provide enough vitamin B1, calcium, iodine, folate, and other key nutrients.
4. Pay Attention to Hydration & Electrolytes
Many studies have shown that electrolyte disturbances from the ketogenic diet may result in trips to the emergency room (27). Especially at the outset, staying hydrated and paying attention to your electrolyte intake can help fend off keto flu symptoms.
5. Be Willing To Make Changes
These diets are not for everyone. If you’re not seeing the desired results, be willing to make the necessary changes.

What’s the Ideal Diet for Humans?
If you’re still not convinced about the ketogenic or carnivore diet, consider the animal-based diet instead. This way of eating consists of high-quality animal foods such as meat, organs, eggs, raw dairy, fruit, honey, and other low-toxicity plant foods.
The animal-based diet is similar to carnivore and keto, but it does not restrict carbohydrates and can be much more inviting to athletes and those looking to maximize their exercise performance. Given the added variety, an animal-based diet can be more enjoyable and sustainable.
It’s also a popular tool for improving gut health, weight loss, and much more.
Fat Loss Stack
Grass-Fed Organs for Metabolic Health
The Choice is Yours
It’s an unfortunate reality, but countless people are struggling with health challenges like obesity, gut issues, or autoimmune diseases. For many, the keto vs carnivore debate is a logical landing point to try to improve these issues without relying on medication.
Even though the short-term benefits can be amazing, the carnivore and keto diets usually wind up being a stepping stone for the typical health journey on the way to a more sustainable and balanced way of eating, like the Animal-Based Diet. While diet is only one component, it’s possible to break free from your health issues without all of the rules and restrictions.
Subscribe to future articles like this:

